Nice Tips About How To Deal With A Spill Of Weak Acid Or Alkali
![a AlkaliLCC [68, 118] and b acid/alkaliLCC [55, 120] degradation](https://i1.rgstatic.net/publication/336793507_Material_Properties_Analysis_of_Acid-alkali_Resistance_Geosynthetics_for_Highway/links/5db25253a6fdccc99d94a77a/largepreview.png)
One of the jobs of a chemist is to tell the.
How to deal with a spill of weak acid or alkali. This planning must be done in advance, not after. A strong base is one which dissociates completely. Contents of the spill kits and how to use each item, and the procedure to effectively deal with spills, including those that are out of the department’s control.
02:58 acids and alkalis are common in daily life. You must wash off any spills with plenty of water, otherwise your skin may soon feel as. Due to acid's corrosive nature, many spill containment materials are ineffective.
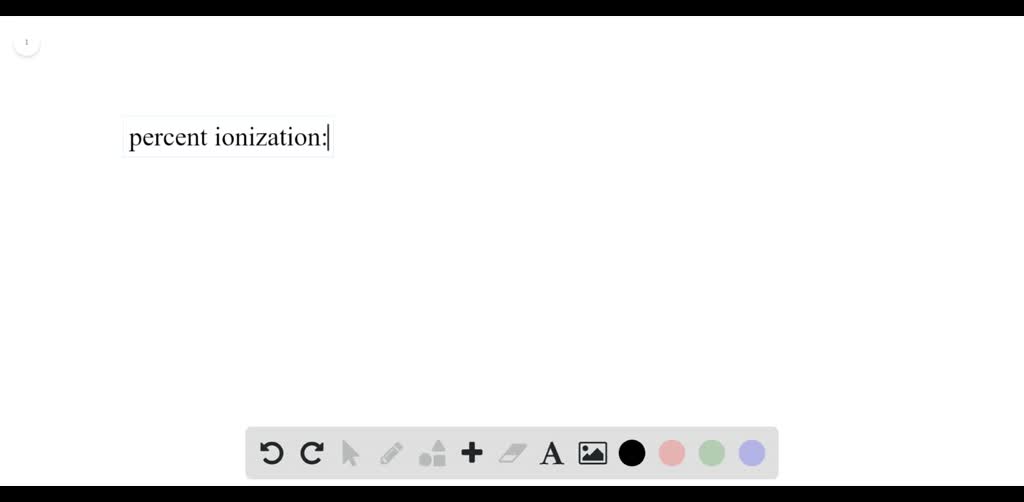
Neutralize acids or bases (alkaline) according to the manufacturer's or supplier's instructions. Calculate the ph or poh. Xh↽−−⇀ xx− +hx+ x h ↽ − − ⇀ x x − + h x +.
If an ion derives from a weak acid, it will make. If an acid is not listed here, it is a weak acid. Tackle a fire or control spills and leaks (when it is safe to do so);
How to deal with a spill of weak acid or alkali. Handling acid spills requires special care and the right tools. Students should be able to:.
They are found in the home, in our bodies, in industry, car batteries and school science labs. A weak acid in water dissociates reversibly as follows: Leave at least 20% air space in bottles of liquid waste.
Examples of corrosive substances include strong acids or strong bases (alkalis), or concentrated solutions of certain weak acids and weak bases. It may be 1% ionized or 99%. If you spill something like hydrofluoric or perchloric acid, you run.
Either way, you will produce less heat if you neutralize with a weak base instead of a strong base. A base that can dissolve in water is also called an alkali. Calculate ph and poh of a weak acid or base solution using simple formula, quadratic equation, and including autoionization of water.
The objective of this guide is to provide laboratory employees with a framework for spill response planning. Evacuate the site, and if necessary nearby premises. As it turns out, there are very few strong acids, which are given in table 14.7.1.
Ka is the dissociation constant for a weak acid: Weak acids and weak bases dissociate only slightly in aqueous solution. Please note, however, these are not intended for use in spills.





![a AlkaliLCC [68, 118] and b acid/alkaliLCC [55, 120] degradation](https://www.researchgate.net/publication/327967502/figure/fig11/AS:963549123862560@1606739421431/a-Alkali-LCC-68-118-and-b-acid-alkali-LCC-55-120-degradation-procedure.png)



/glass-beakers-indicating-blue-for-weak-alkali-level--green-for-strong-alkali-level--and-red-for-weak-acidity-level-87997927-570914e93df78c7d9ed6d099.jpg)







